Rail anchors and plates are critical components in railway infrastructure, playing a vital role in maintaining track stability and ensuring the safe and efficient operation of trains. Rail anchors, also known as anti-creepers, are devices attached to the rail base to prevent longitudinal movement of the rails, which can be caused by temperature changes, train braking, and other dynamic forces . Rail plates, often referred to as tie plates or base plates, are steel plates placed between the rail and the sleeper (or tie) to distribute the load from the rail to the tie, thereby reducing wear and enhancing track stability .
Importance in Railway Track Stability and Maintenance

The primary function of rail anchors and plates is to maintain the correct alignment and gauge of the railway track, which is essential for the safe passage of trains. By preventing rail movement and distributing loads evenly, these components help to reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of the track infrastructure .
Types of Rail Anchors
Detailed Descriptions of Different Types of Rail Anchors
Rail anchors can be broadly categorized into two main types: drive-on anchors and spring-type anchors.
- Drive-on Anchors: These are heavy-duty, one-piece steel anchors that are driven onto the rail base using a hammer or specialized machinery. They exert an anti-creeping force against the edge of the tie to resist rail movement. Drive-on anchors are commonly used in areas with heavy train traffic and are known for their durability and ease of installation .
- Spring-type Anchors: These anchors are also made from heat-treated steel and are designed to be fastened to the rail base. They provide a spring-like action that helps to absorb dynamic forces and prevent rail movement. Spring-type anchors are suitable for both manual and mechanized application and can be removed and reapplied without significant loss of anchoring capability .
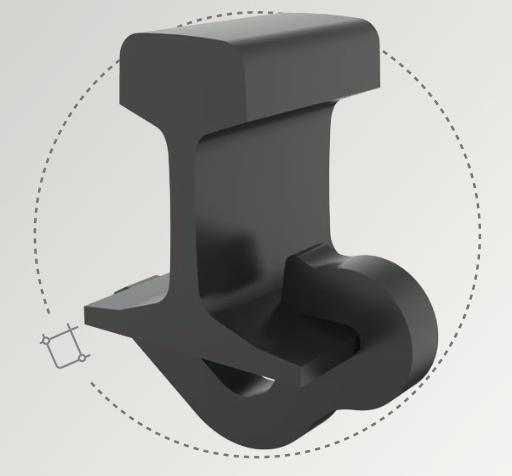


Applications and Benefits of Each Type
- Drive-on Anchors: Ideal for mainline tracks, branch lines, turnouts, bridges, switches, and crossings. They offer high holding power and are effective in reducing rail buckling stresses and maintaining rail gaps .
- Spring-type Anchors: Suitable for areas with frequent temperature fluctuations and heavy axle loads. They provide consistent holding power and are easy to install and maintain, making them a versatile choice for various track conditions .
Types of Rail Plates
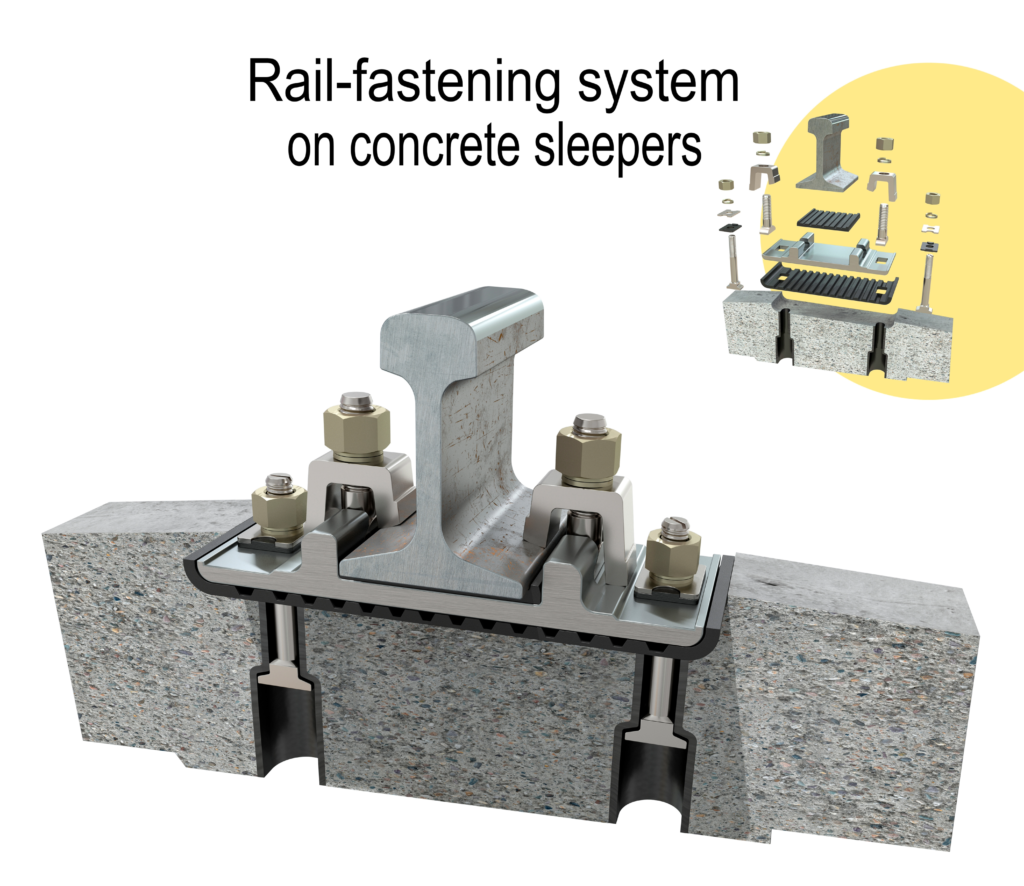
Overview of Different Types of Rail Plates
Rail plates, or tie plates, come in various designs to suit different rail and sleeper configurations. The main types include:
- Single Shoulder Tie Plates: These plates have one raised edge to fit against one side of the rail base. They are typically used for lighter rail sections and are suitable for a wide range of rail widths .
- Double Shoulder Tie Plates: Featuring two raised edges, these plates provide a more secure fit for the rail. They are commonly used for heavier rail sections and offer better load distribution .
- Hook Twin Tie Plates: Designed for use in turnouts and special trackwork, these plates have slotted holes and work in pairs to secure the rail and maintain correct spacing .
Material Composition and Design Variations
Rail plates are generally made from hot-rolled, cast, or forged steel. The choice of material and manufacturing process depends on the specific requirements of the track, such as load-bearing capacity and environmental conditions. Design variations include different hole patterns, shoulder configurations, and thicknesses to accommodate various rail sizes and applications .
Functions and Benefits
Explanation of How Rail Anchors and Plates Contribute to Track Stability
Rail anchors and plates work together to maintain the stability and alignment of railway tracks. Anchors prevent longitudinal rail movement, while plates distribute the load from the rail to the tie, reducing stress and wear on the track components. This combination ensures that the rails remain securely in place, even under heavy loads and dynamic forces .
Benefits in Reducing Track Movement and Enhancing Safety
By preventing rail movement and ensuring even load distribution, rail anchors and plates help to reduce the risk of track misalignment, which can lead to derailments and other safety hazards. They also minimize the need for frequent maintenance, thereby reducing operational costs and improving the overall reliability of the railway system .
Manufacturing Process
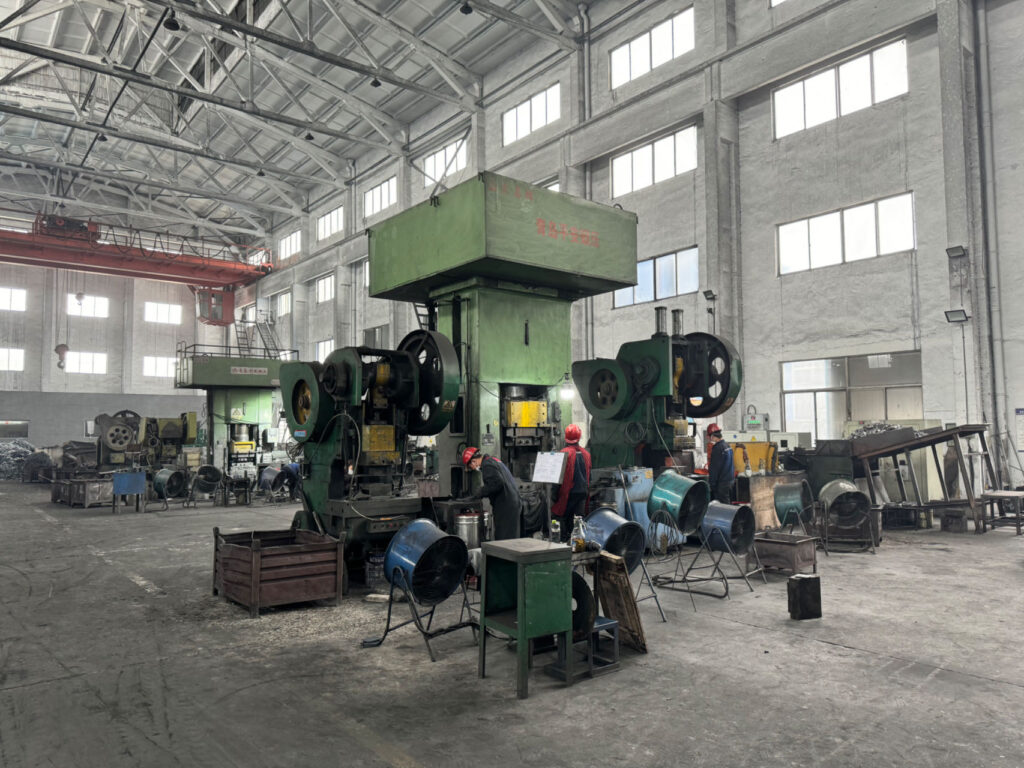

Detailed Description of the Manufacturing Process for Rail Anchors and Plates
The manufacturing process for rail anchors and plates involves several steps, including material selection, forming, heat treatment, and finishing. High-quality steel is typically used, and the components are formed using hot-rolling, casting, or forging techniques. Heat treatment is applied to enhance the strength and durability of the components, followed by precision machining to achieve the required dimensions and tolerances .
Quality Control Measures and Standards

Quality control is critical in the manufacturing of rail anchors and plates. Standards such as those set by the American Railway Engineering and Maintenance-of-Way Association (AREMA) ensure that the components meet stringent performance and safety criteria. Regular inspections and testing are conducted to verify the mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and overall quality of the products .
Installation and Maintenance
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Rail Anchors and Plates
- Preparation: Ensure that the rail and tie surfaces are clean and free of debris.
- Positioning: Place the tie plate on the tie, aligning it with the rail base.
- Securing the Plate: Use rail bolts or spikes to secure the tie plate to the tie.
- Installing the Anchor: Position the rail anchor against the rail base and tie, then drive it into place using a hammer or specialized tool.
- Inspection: Check the installation to ensure that the components are securely fastened and properly aligned .
Best Practices for Maintenance and Inspection
Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of rail anchors and plates. Key practices include:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Tightening: Ensure that all bolts and spikes are properly tightened.
- Replacement: Replace any worn or damaged components promptly to prevent track instability .
Tools and Equipment Needed for Installation
Common tools and equipment used for installing rail anchors and plates include hammers, wrenches, rail pullers, and specialized machinery for mechanized installation. Proper safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection, is also essential .
Innovations and Technology
Recent Advancements in Rail Anchor and Plate Technology
Recent advancements in rail anchor and plate technology include the development of new materials and designs that enhance performance and durability. Innovations such as high-strength alloys, improved heat treatment processes, and advanced manufacturing techniques have led to components that offer better resistance to wear and environmental conditions .
New Materials and Designs Improving Performance and Durability
New materials, such as high-strength steel and composite materials, are being used to manufacture rail anchors and plates. These materials offer superior mechanical properties and longer service life. Additionally, innovative designs, such as elastic rail anchors and advanced tie plate configurations, provide better load distribution and vibration absorption, further enhancing track stability and safety .
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Examples of Successful Rail Anchor and Plate Installations
Several railway companies have reported successful installations of rail anchors and plates, highlighting the benefits of these components in improving track stability and reducing maintenance costs. For example, the use of compression anchors on mainline tracks has significantly reduced rail movement and maintenance requirements, leading to improved operational efficiency .
Testimonials from Railway Companies or Case Studies Highlighting the Benefits
Railway companies have provided positive feedback on the performance of modern rail anchors and plates. Testimonials often emphasize the increased track stability, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced safety provided by these components. Case studies also demonstrate the effectiveness of new materials and designs in real-world applications, showcasing the tangible benefits of these innovations .
Common Issues and Solutions
Common Problems Encountered with Rail Anchors and Plates
Common issues with rail anchors and plates include wear and corrosion, improper installation, and component failure due to excessive loads or environmental conditions. These problems can lead to track instability and increased maintenance requirements .
Solutions and Troubleshooting Tips
To address these issues, it is important to follow best practices for installation and maintenance, use high-quality components, and conduct regular inspections. Troubleshooting tips include:
- Regular Inspections: Identify and address wear and damage early.
- Proper Installation: Ensure that components are installed correctly and securely.
- Use of High-Quality Materials: Select components made from durable materials that meet industry standards .
Environmental and Economic Impact
Analysis of the Environmental Benefits of Using High-Quality Rail Anchors and Plates
High-quality rail anchors and plates contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement. This leads to lower resource consumption and waste generation. Additionally, improved track stability reduces the risk of derail
ments and other incidents that can have significant environmental impacts .
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Economic Benefits
Investing in high-quality rail anchors and plates can result in significant long-term economic benefits. These components reduce maintenance costs, extend the lifespan of the track infrastructure, and improve operational efficiency. The initial investment in high-quality components is often offset by the savings in maintenance and replacement costs over time .
Compliance and Standards
Overview of Industry Standards and Regulations
Rail anchors and plates must comply with various industry standards and regulations to ensure their performance and safety. Key standards include those set by the American Railway Engineering and Maintenance-of-Way Association (AREMA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards specify the material properties, design requirements, and testing procedures for rail components .
Importance of Compliance for Safety and Reliability
Compliance with industry standards is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of railway tracks. Adhering to these standards helps to prevent component failure, reduce maintenance requirements, and enhance the overall performance of the railway system. It also ensures that the components are compatible with other track infrastructure and can withstand the demanding conditions of railway operations .
In conclusion, rail anchors and plates are indispensable components of railway infrastructure, providing essential support and stability to the tracks. Advances in materials and design continue to improve their performance and durability, contributing to safer and more efficient railway operations.
For more information and to explore high-quality rail anchors and plates, visit Starpath Railroad Material Supply. Our commitment to quality and compliance with industry standards ensures that our products meet the highest performance and safety criteria.
References
- Starpath Rail Clip
- Starpath Tie Plate
- Starpath AREMA Improved Anchor
- Starpath AREMA Standard Railway Products
- Starpath High Volume Forging
- Starpath Custom Built Manufacturing
- Starpath Advanced Powder Metallurgy Solutions
- About Starpath – Top Railroad Material Supplier
- Contact Starpath
- Request a Quote from Starpath
By ensuring that your railway infrastructure is equipped with the best rail anchors and plates, you can achieve enhanced track stability, reduced maintenance costs, and improved safety for your railway operations.

